Key Concepts in Database Management: A Beginner's Guide
Understanding the Different Types of DBMS Keys
what is key in DBMS?
A Key is a field or set of fields used to uniquely identify any record or row of data from a table and establish a relationship between tables. There are several types of keys that can be used in DBMS including:
Primary Key
Foreign Key
Composite key
Candidate key
Alternate key
Surrogate key
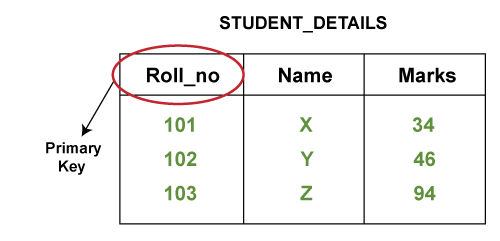
Primary key
A primary key is an attribute or column that can uniquely identify each row or record of a table. It can not contain a null value, and there can be only one primary key per table.
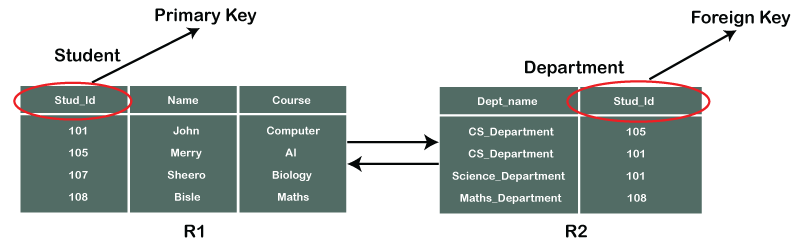
Foreign Key
A foreign key is a field or attribute in one table that refers to a primary key in another table. It is used to establish the relationship between two tables and can be used to enforce data integrity.
Composite key
A composite key made by more than one attribute or column that can uniquely identify a row in a table. It is used when no single column can identify a row in the table.
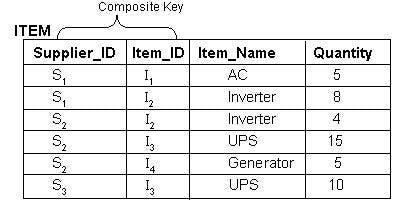
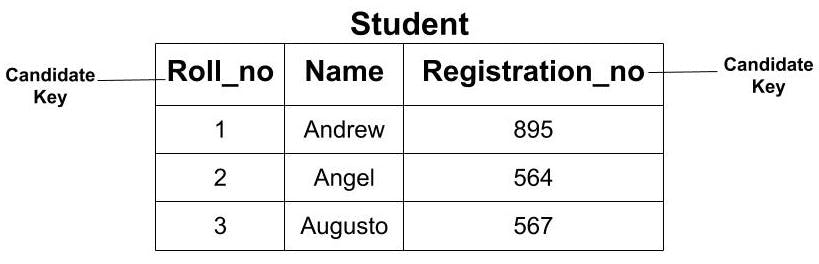
Candidate key
A candidate key is an attribute or set of attributes that could be used as a primary key. A table can have multiple candidate keys, but only one of them can be chosen as a primary key.
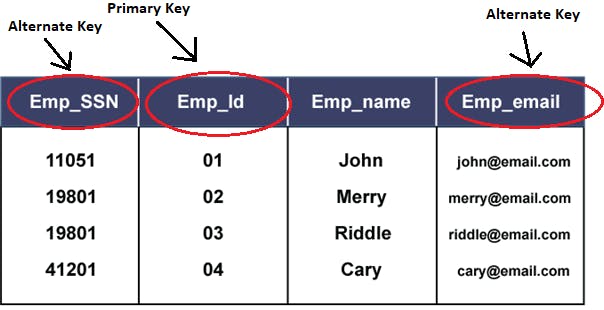
Alternate key or Secondary key
An alternate key or secondary key is a candidate key that is not used as a primary key, but that can still use to uniquely identify a row in a table.
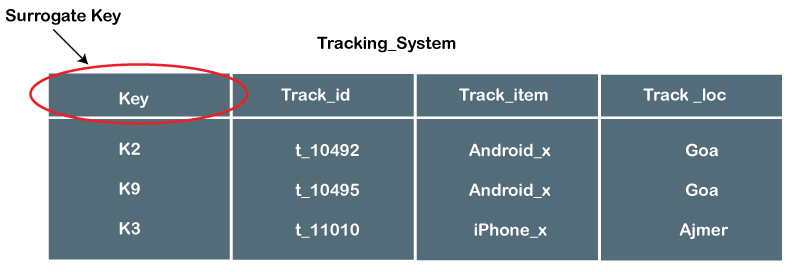
Surrogate key
A surrogate key is a synthetic primary key that is used to uniquely identify a row in a table. it is typically an auto-incrementing integer or random alphanumeric string. And it is used when the natural primary key is not able to identify a row in a table.